G Protein Linked Receptors Whereas Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
G-protein-linked receptors _____ whereas receptor tyrosine kinases _____. Originally these systems were thought to act in isolation but it has become increasingly clear over the past decade that there are complex interac-.

Cell Signaling By Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Cell
We found that a range of chemoattractants activating G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs receptor tyrosine kinases RTKs and Toll-likeIL-1 receptors TLRIL1Rs unexpectedly initiate.

. Whereas ligand bias has been studied primarily for G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs there are also reports of ligand bias for receptor tyrosine kinases RTKs. Act by phosphorylating a protein. The hormone epinephrine binds to a specific receptor on the plasma membrane of the liver cell.
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase Akt protein kinase B and the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. It reflects differences in the responses of a receptor to specific ligands and has implications for the development of highly specific therapeutics. Are not enzymes.
G protein-coupled receptor kinases. More than just kinases and not only for GPCRs. New evidence suggests that these two receptor types independently control different pathways leading to Ras activation in response to lysophosphatidic acid LPA.
A hormone binds to an intracellular receptor. Here we clarify the role of p70S6 kinase p70S6K as an integrator of receptor tyrosine kinase and GPCR signaling that augments ASM DNA. Regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors by non-receptor tyrosine kinases such as.
Whereas ligand bias has been studied primarily for G proteincoupled receptors GPCRs there are also reports of ligand bias for receptor tyrosine kinases RTKs. G-protein-linked receptors _____ whereas receptor tyrosine kinases _____. What is the general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from.
G-protein-linked receptors _____ whereas receptor tyrosine kinases _____. G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 GRK5 is a ubiquitously expressed member of the GRK family of SerThr kinases originally characterized for their ability to phosphorylate agonist-activated 7-transmembrane receptors. EText Concept 112 A.
Pharmacology Therapeutics 2012. Receptor tyrosine kinase proteins form a dimer. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package.
GDP displaces GTP on the G protein. Open an ion channel when bound to a signal molecule B. Certain yeast cells secrete a molecule called the -factor.
Are transmembrane proteins. The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Protein Superfamily Receptor tyrosine kinases RTKs play essential roles in the cellular communication network that orchestrates the development of metazoans. More than 700 genes have been identified as G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs which form the largest protein superfamily in the human genome 1GPCRs play key roles in mediating a wide variety of physiological events from hormonal responses to sensory modulation vision olfaction and taste 2 3GPCR-targeting drugs are used to treat.
G-protein-linked receptors _____ whereas receptor tyrosine kinases _____. The binding of a signal molecule to a ligand-gated ion channel _____. Include the G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs recep-tor tyrosine kinases RTKs cytokine receptor-activated kinases and members of the steroidthyroid hormone receptor superfamily.
Cross-talk between G-protein-coupled receptors and tyrosine kinases can occur at several levels including the receptor-to-receptor level and at crucial down-stream points eg. 1 GRK5 can regulate signaling through numerous 7-transmembrane receptors 12 several of which have been implicated in atherogenesis. A ligand binds to a receptor tyrosine kinase.
Act by phosphorylating a protein. An ion-gated channel opens. What did Sutherland discover about glycogen metabolism in liver cells.
Which of the following is activated when the binding of single molecules causes it to form a dimer. Which of the following statements describes the function of. However the understanding of RTK ligand bias is lagging behind the knowledge of GPCR ligand bias.
Tumor inflammation promotes angiogenesis immunosuppression and tumor growth but the mechanisms controlling inflammatory cell recruitment to tumors are not well understood. G-protein-linked receptors _____ whereas receptor tyrosine kinases _____. 37 Full PDFs related to this paper.
Have enzymatic function Testosterone and estrogen are lipid-soluble signal molecules that cross the plasma membrane by simple diffusion. G-protein-coupled receptors _____ whereas receptor tyrosine kinases _____. In some cases the receptor tyrosine kinases phosphorylate G protein-coupled receptors whereas in others phosphoinositide 3-kinase protein kinase B and protein kinase C are key elements in these crosstalks.
Are not enzymes. We have previously demonstrated that concomitant activation of receptor tyrosine kinases and certain G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs can promote a synergistic increase in the rate of airway smooth muscle cell ASM proliferation. Are found only on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane C.
Are transmembrane proteins. Stimulate an a yeast cell to grow toward the cell. After a signaling molecule binds to a G protein-coupled receptor what activates the associated G protein.
G-protein-coupled receptors and protein tyrosine kinases represent two prominent pathways for cellular signaling. Ras protein regulation by G-protein-coupled receptors has been thought to occur through transactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Epidermal growth factor receptor function is needed for basal.
As our knowledge of cell signaling pathways mediated by the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors and the smaller family of receptor tyrosine kinases expands so does our appreciation of how these two major signaling platforms share. GTP displaces GDP on the G protein. Open an ion channel when bound to a signal molecule b.
Two paracrine autocrine processes also participate ie epidermal growth factor transactivation and sphingosine 1-phosphate generation and signaling. Are found only on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane c. A short summary of this paper.
They are a major class of enzyme-coupled cell surface receptors activated when bound by extracellular signals from the environment such as growth factors. The purpose of this molecule is to _____.

Igf 1r As A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Rtk G Protein Coupled Receptors Download Scientific Diagram
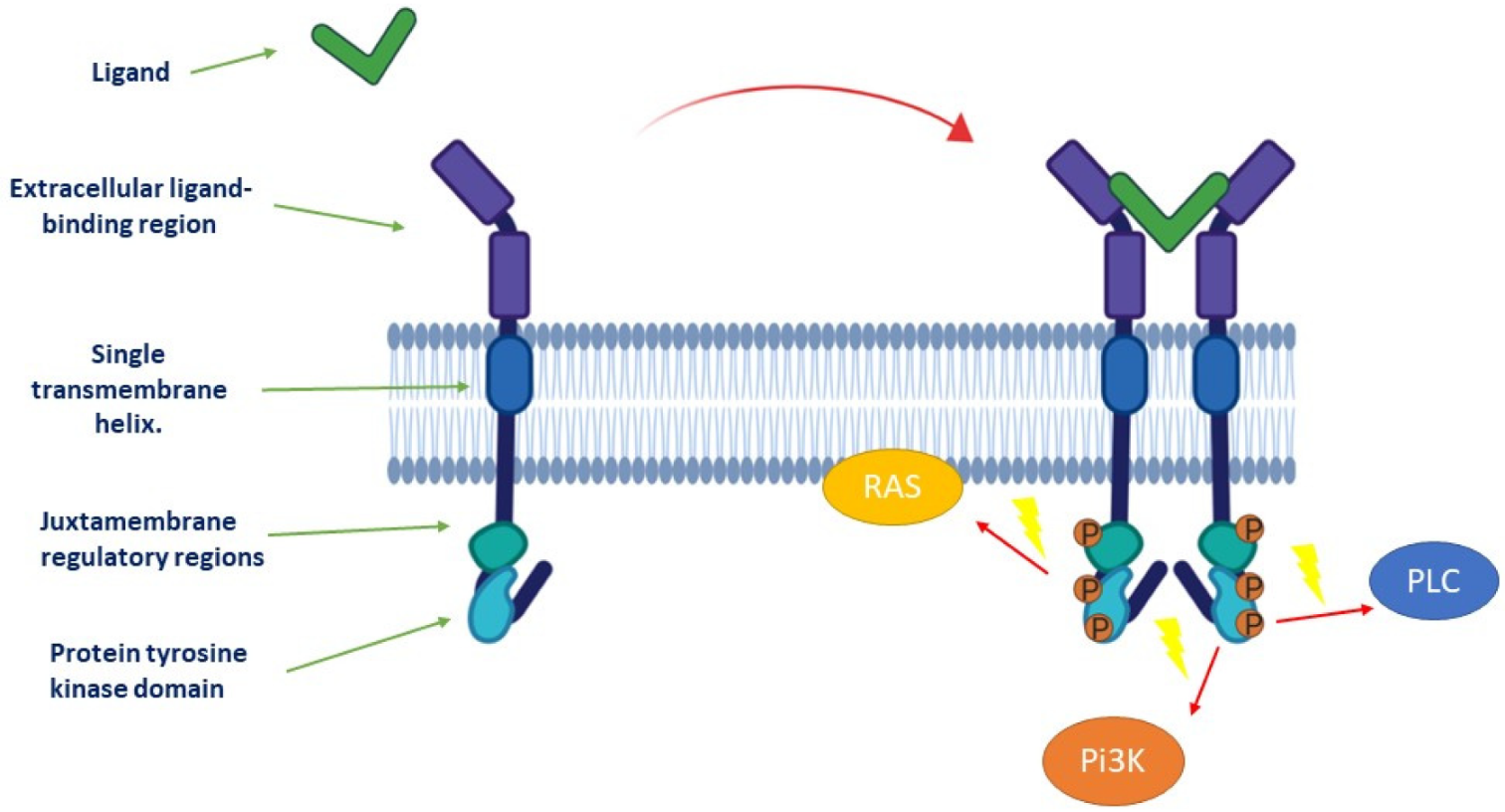
Cancers Free Full Text Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors In Cancer Breakthrough And Challenges Of Targeted Therapy Html
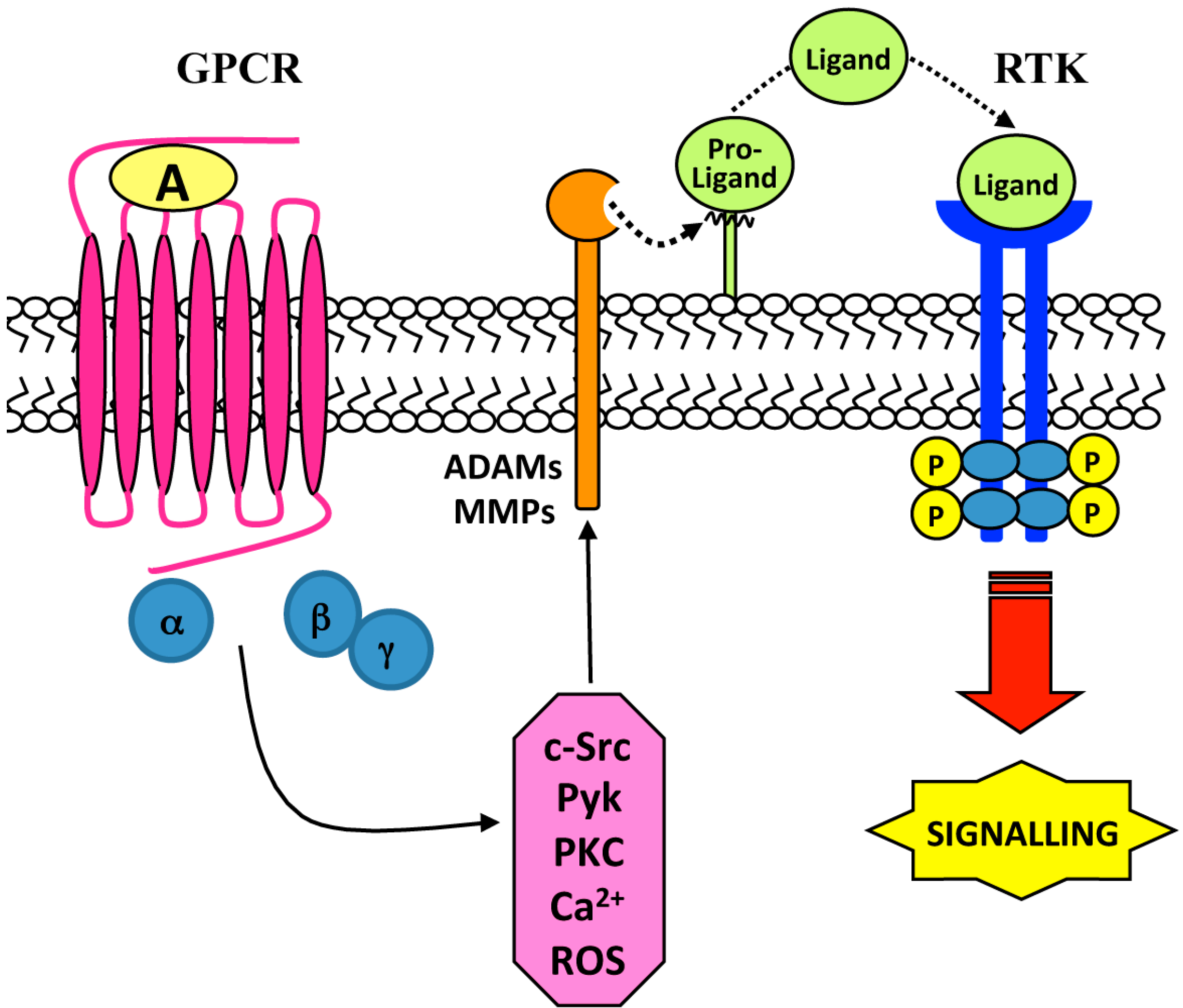
Ijms Free Full Text Cell Surface Receptors Transactivation Mediated By G Protein Coupled Receptors Html

Difference Between G Protein Linked Receptors And Enzyme Linked Receptors Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
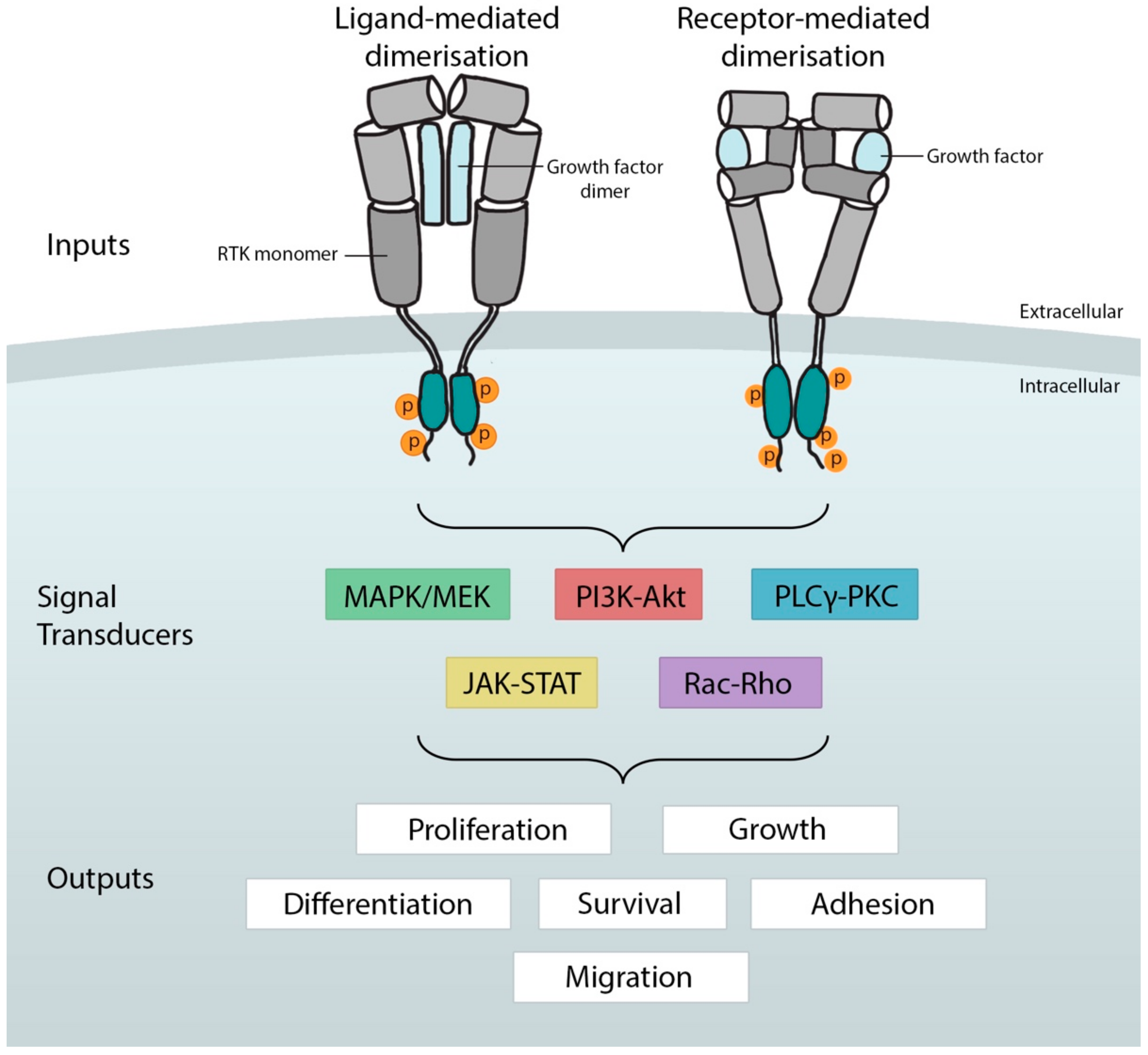
Ijms Free Full Text Receptor Tyrosine Kinases In Development Insights From Drosophila Html

Neurotransmitter Receptors In Cell Signaling Transduction Sino Biological

Difference Between G Protein Coupled Receptors And Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Difference Between G Protein Coupled Receptors And Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Mechanisms Of Receptor Tyrosine Protein Kinase Erbb 3 Erbb3 Action In Human Neoplasia The American Journal Of Pathology

Enzyme Linked Receptor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
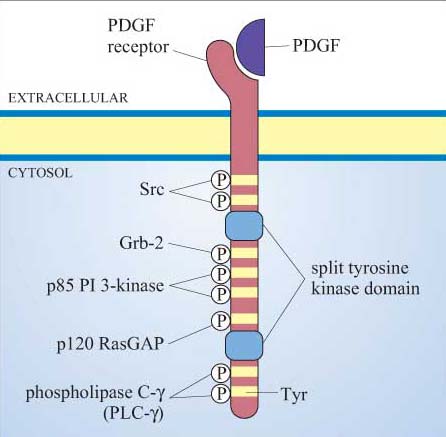
Cell Signalling Openlearn Open University
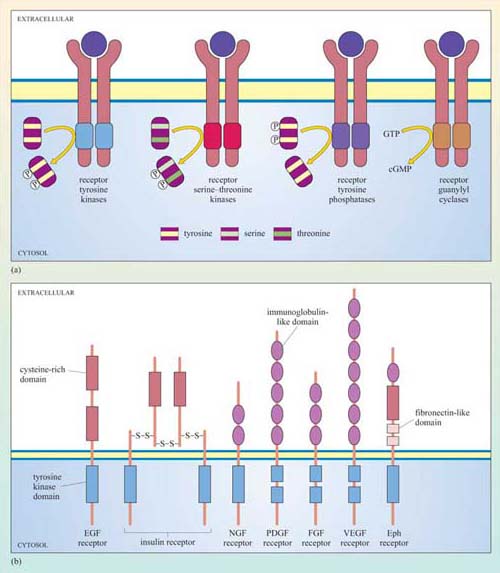
Cell Signalling Openlearn Open University

Protein Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Pathways Are Potential Targets In Download Scientific Diagram

G Protein Coupled Receptors And Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Youtube

Schematic Representation Of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase And Downstream Download Scientific Diagram

Receptors That Are Catalytic Signal Transduction Physiology Of Cells And Molecules Medical Physiology 3rd Edition

Igf 1r As A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Rtk G Protein Coupled Receptors Download Scientific Diagram

Tyrosine Kinase Receptors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Different Mechanisms Of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Rtk Transactivation Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment